Private Placement Foster Care Injury: A Complete Guide to Risks, Rights, and Legal Options
Introduction to Private Placement Foster Care Injury
A private placement foster care injury refers to physical, emotional, or psychological harm suffered by a child placed into foster care through a private agency, individual arrangement, or non-governmental organization. Unlike public foster care systems managed directly by state agencies, private placement foster care often involves private adoption agencies, faith-based organizations, or licensed third-party providers.
While many private foster placements are safe and nurturing, injuries still occur—and when they do, they raise complex questions about responsibility, oversight, and accountability. Understanding how and why these injuries happen is essential for foster parents, biological families, agencies, and legal advocates alike.
This comprehensive guide explains the causes of private placement foster care injury, the legal rights of injured children, prevention strategies, and what steps to take when harm occurs.
Understanding Private Placement Foster Care
Private placement foster care is an arrangement where a child is placed with foster parents through a private entity rather than a government-run child welfare agency. These placements are often chosen for reasons such as:
-
Faster placement timelines
-
Specialized care needs
-
Religious or cultural alignment
-
Adoption-focused foster care
Although private agencies must follow licensing laws, oversight can vary widely. This variability can increase the risk of a private placement foster care injury if standards are not consistently enforced.
Types of Injuries in Private Placement Foster Care
Injuries in private foster care settings fall into several categories. Each type requires a different response and carries unique legal implications.
1. Physical Injuries
Physical harm is the most visible form of private placement foster care injury and may include:
-
Bruises, fractures, or burns
-
Malnutrition or dehydration
-
Injuries from unsafe living conditions
These injuries may result from abuse, neglect, or lack of proper supervision.
2. Emotional and Psychological Injuries
Not all injuries leave visible marks. Emotional harm can be just as damaging and often includes:
-
Anxiety or depression
-
Attachment disorders
-
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Children who experience instability or mistreatment in foster placements are especially vulnerable to emotional trauma.
3. Medical Neglect
Medical neglect occurs when foster parents or agencies fail to:
-
Provide prescribed medications
-
Attend medical appointments
-
Respond to chronic or urgent health needs
Medical neglect is a serious form of private placement foster care injury and may lead to long-term complications.
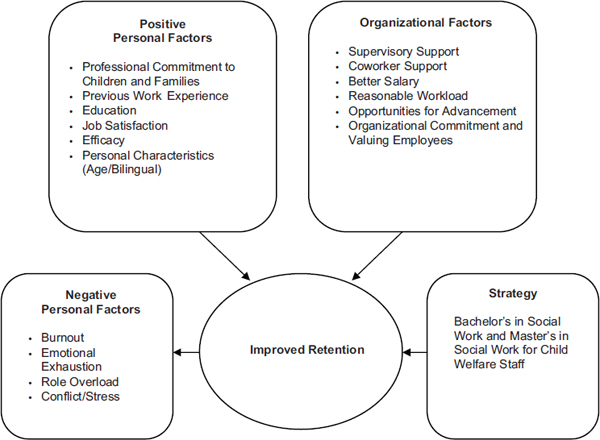
Common Causes of Private Placement Foster Care Injury
Understanding the root causes of injury helps prevent future harm.
Inadequate Screening of Foster Parents
Private agencies may face pressure to place children quickly, leading to insufficient background checks or home evaluations.
Lack of Training and Support
Foster parents may not receive adequate training in:
-
Trauma-informed care
-
Managing behavioral challenges
-
Child development and safety
Without proper preparation, even well-meaning caregivers can unintentionally cause harm.
Poor Oversight and Monitoring
Some private placements lack regular home visits or follow-ups. This absence of supervision increases the risk of undetected abuse or neglect.
Who Is Legally Responsible for a Private Placement Foster Care Injury?
Determining liability in a private placement foster care injury case can be complex. Responsibility may fall on one or more parties.
Foster Parents
If an injury results from abuse, neglect, or reckless behavior, foster parents may be held directly liable.
Private Placement Agencies
Agencies can be responsible if they:
-
Failed to properly screen foster parents
-
Ignored warning signs of abuse
-
Did not comply with licensing or safety regulations
Medical or Educational Providers
In some cases, third parties such as doctors or schools may share liability if they failed to report suspected abuse.
Legal Rights of Children Injured in Private Foster Care
Children in private foster placements have the same fundamental rights as those in public systems, including:
-
The right to a safe living environment
-
The right to medical and mental health care
-
The right to be free from abuse and neglect
When a private placement foster care injury occurs, legal action may be taken to protect the child and seek compensation for damages.
Signs of Abuse or Neglect in Private Foster Placements
Early detection can save lives. Warning signs include:
-
Unexplained injuries
-
Sudden changes in behavior
-
Fear of caregivers
-
Poor hygiene or untreated medical issues
Anyone who suspects a private placement foster care injury should report concerns immediately to child protective services or appropriate authorities.
Steps to Take If a Private Placement Foster Care Injury Occurs
1. Ensure Immediate Safety
Remove the child from harm and seek medical attention if needed.
2. Document Everything
Keep records of:
-
Injuries and medical reports
-
Photos (if appropriate)
-
Dates, times, and witness statements
3. Report the Injury
Notify child welfare authorities and any relevant oversight bodies.
4. Seek Legal Guidance
An experienced attorney can help determine liability and protect the child’s rights.
Prevention of Private Placement Foster Care Injury
Preventing injury is always better than responding after harm occurs.
Stronger Screening Processes
Thorough background checks and home studies reduce risk.
Ongoing Training
Foster parents should receive continuous education in:
-
Child safety
-
Trauma-informed care
-
Emergency response
Regular Monitoring
Unannounced home visits and child interviews help identify problems early.
The Role of Advocacy and Oversight
Independent advocates play a critical role in reducing private placement foster care injury. These advocates:
-
Monitor child well-being
-
Speak up when systems fail
-
Ensure children’s voices are heard
Community awareness and accountability are essential to improving private foster care systems.
Long-Term Impact of Private Placement Foster Care Injury
Injuries sustained in foster care can have lifelong consequences, including:
-
Chronic health issues
-
Difficulty forming relationships
-
Educational challenges
Early intervention, therapy, and stable placements can significantly improve outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a private placement foster care injury?
A private placement foster care injury is any physical, emotional, or medical harm suffered by a child placed through a private foster care arrangement.
2. Are private foster care agencies regulated?
Yes, but regulations vary by jurisdiction, and oversight may be less consistent than in public systems.
3. Who can be held liable for a private placement foster care injury?
Liability may include foster parents, private agencies, or third parties depending on the circumstances.
4. What should I do if I suspect a foster child is injured?
Report concerns immediately to child protective services and ensure the child’s safety.
5. Can emotional trauma count as a foster care injury?
Yes. Emotional and psychological harm are recognized forms of injury.
6. How can private placement foster care injury be prevented?
Through better screening, training, monitoring, and advocacy.
Conclusion
A private placement foster care injury is a serious issue that demands attention, accountability, and compassion. While private foster care can provide loving homes and positive outcomes, failures in oversight or care can place vulnerable children at risk.
By understanding the causes, recognizing warning signs, enforcing legal protections, and prioritizing prevention, communities can help ensure that every child in private foster care is safe, supported, and given the chance to heal and thrive.
 Chicago Medical Malpractice Lawyers Blog
Chicago Medical Malpractice Lawyers Blog